High-performance work systems are characterized by high employee turnover, a paradoxical phenomenon that has sparked considerable debate and research. This opening paragraph provides a concise overview of the topic, highlighting the intriguing relationship between high performance and employee attrition.
The following paragraphs delve into the complexities of high-performance work systems, exploring their defining characteristics, the reasons behind high employee turnover, and strategies for mitigating it. Case studies of successful HPWS implementations are also presented, offering valuable insights into real-world applications.
Defining High-Performance Work Systems: High-performance Work Systems Are Characterized By High Employee Turnover

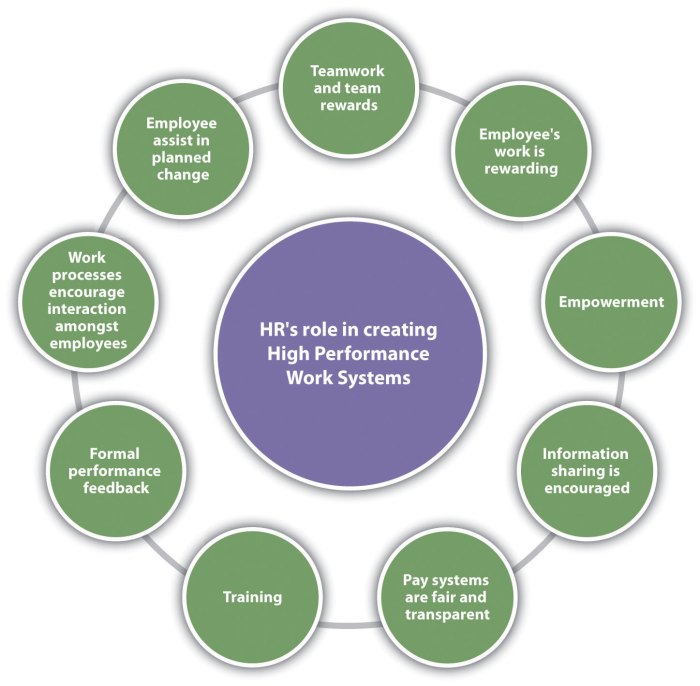
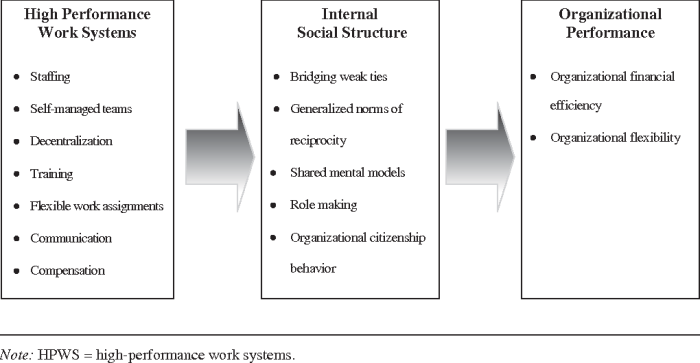
High-performance work systems (HPWS) are organizational structures and practices designed to enhance employee performance and organizational effectiveness. They are characterized by:
- Employee empowerment and autonomy
- Team-based work and collaboration
- Flexible work arrangements
- Performance-based rewards
- Continuous learning and development
Organizations that have successfully implemented HPWS include Google, Amazon, and Toyota.
Employee Turnover in HPWS, High-performance work systems are characterized by high employee turnover
Data suggests that employee turnover rates in HPWS are generally higher than in traditional work systems. Potential reasons for this include:
- Higher expectations and workload
- Increased accountability and pressure
- Lack of work-life balance
Benefits and Challenges of HPWS
Benefits
HPWS can offer several benefits, including:
- Increased productivity and innovation
- Improved employee engagement and satisfaction
- Enhanced organizational adaptability and resilience
Challenges
Implementing and maintaining HPWS can pose challenges, such as:
- Cultural resistance and change management
- Resource constraints and financial implications
- Measuring and evaluating performance effectively
Strategies to Reduce Turnover in HPWS
To reduce employee turnover in HPWS, organizations can implement strategies such as:
| Strategy | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Flexible work arrangements | Improved work-life balance and reduced burnout |
| Comprehensive onboarding and training | Enhanced employee engagement and job satisfaction |
| Regular performance reviews and feedback | Increased transparency and opportunities for growth |
| Mentoring and coaching programs | Improved employee development and retention |
| Employee recognition and rewards | Motivation and appreciation for contributions |
Case Studies of HPWS Implementation
Successful HPWS implementations include:
| Organization | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Empowerment, collaboration, performance-based rewards | |
| Amazon | Data-driven decision-making, continuous improvement |
| Toyota | Lean manufacturing, employee involvement, kaizen |
FAQs
Why do high-performance work systems often experience high employee turnover?
HPWS can be demanding environments that require employees to work long hours, handle high workloads, and adapt to constant change. This can lead to burnout, stress, and dissatisfaction, contributing to increased turnover.
What are some strategies for reducing employee turnover in HPWS?
Organizations can implement strategies such as providing competitive compensation and benefits, fostering a positive work culture, offering opportunities for professional development, and addressing employee concerns promptly.
How can organizations balance the benefits of HPWS with the challenge of high employee turnover?
By carefully designing and implementing HPWS, organizations can optimize performance while minimizing turnover. This involves creating a supportive work environment, providing adequate resources, and investing in employee well-being.