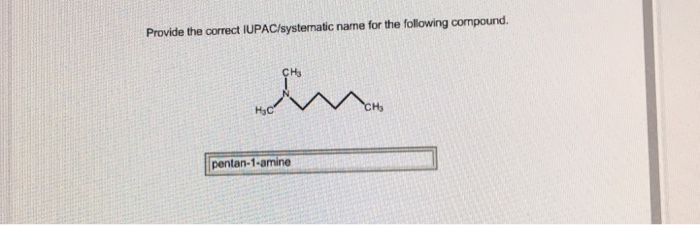
Provide the correct iupac systematic name for the following compound – Embarking on a journey of chemical nomenclature, we delve into the intricacies of providing the correct IUPAC systematic name for a given compound. Understanding and adhering to these systematic naming conventions are paramount in the scientific realm, ensuring clarity and precision in chemical communication.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a set of guidelines for systematically naming organic compounds, providing a standardized language for chemists worldwide. This nomenclature system ensures that each compound is assigned a unique and descriptive name that reflects its structure and composition.
IUPAC Systematic Nomenclature: Provide The Correct Iupac Systematic Name For The Following Compound
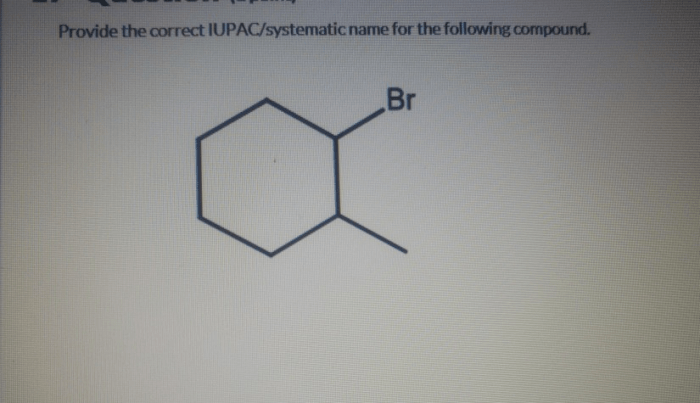
IUPAC systematic nomenclature is a standardized system for naming organic compounds. It is based on the principles of:
- Using prefixes to indicate the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain.
- Using suffixes to indicate the type of functional group present.
- Numbering the carbon atoms in the parent chain so that the functional group has the lowest possible number.
IUPAC systematic names are important because they provide a clear and unambiguous way to identify organic compounds. This is essential for scientific communication and for ensuring that compounds can be synthesized and used safely.
Functional Group Identification
The functional groups present in a compound determine its chemical and physical properties. Common functional groups include:
- Alkanes: Contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms and have the general formula CnH2n+2.
- Alkenes: Contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond and have the general formula CnH2n.
- Alkynes: Contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond and have the general formula CnH2n-2.
- Alcohols: Contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) and have the general formula CnH2n+1OH.
- Ethers: Contain an ether group (-O-) and have the general formula CnH2n+2O.
Functional groups can be identified by their characteristic spectroscopic properties, such as infrared (IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
Structural Analysis
The molecular formula of a compound tells us the number of atoms of each element that are present in the compound. The structural formula shows how the atoms are connected to each other. The molecular geometry of a compound is determined by the hybridization of the atoms in the compound.
Structural analysis can be used to determine the properties of a compound. For example, the polarity of a compound is determined by the distribution of electrons in the molecule.
Isomerism
Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. There are two main types of isomerism:
- Structural isomerism: Occurs when the atoms in the molecule are connected in different ways.
- Stereoisomerism: Occurs when the atoms in the molecule are arranged in different spatial orientations.
Isomerism can have a significant impact on the properties of a compound. For example, structural isomers may have different boiling points and solubilities, while stereoisomers may have different biological activities.
Reaction Chemistry
The reactivity of a compound is determined by its functional groups. Functional groups can undergo a variety of reactions, such as:
- Addition reactions: Involve the addition of an atom or group of atoms to a double or triple bond.
- Substitution reactions: Involve the replacement of an atom or group of atoms with another atom or group of atoms.
- Elimination reactions: Involve the removal of an atom or group of atoms from a molecule.
Reaction chemistry is important for understanding how compounds can be synthesized and used.
Applications

Organic compounds have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine: Organic compounds are used as drugs, antibiotics, and other medical treatments.
- Industry: Organic compounds are used as solvents, plastics, and other materials.
- Materials science: Organic compounds are used as semiconductors, superconductors, and other materials with special properties.
The properties of organic compounds make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
FAQ
What is the purpose of IUPAC systematic nomenclature?
IUPAC systematic nomenclature provides a standardized and unambiguous way to name chemical compounds, ensuring clear and accurate communication among chemists.
How do I determine the IUPAC systematic name for a given compound?
The IUPAC systematic name is derived by identifying the parent chain, functional groups, prefixes, and suffixes according to the IUPAC guidelines.
Why is it important to use IUPAC systematic names?
IUPAC systematic names provide a precise and unambiguous way to identify and describe chemical compounds, facilitating communication and avoiding confusion.