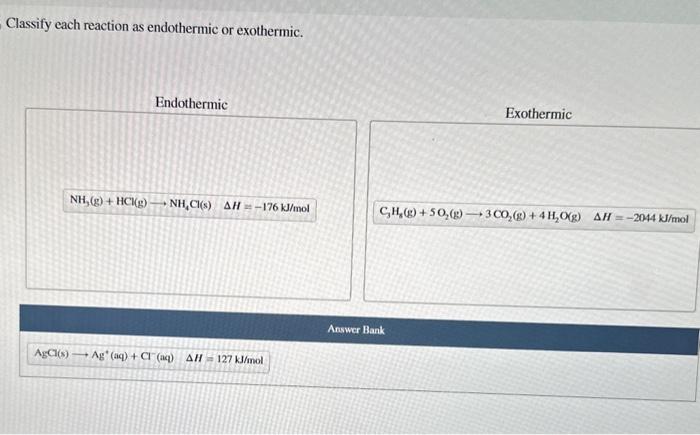
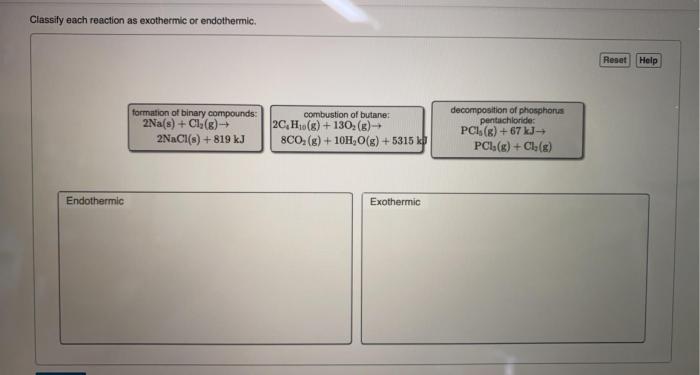
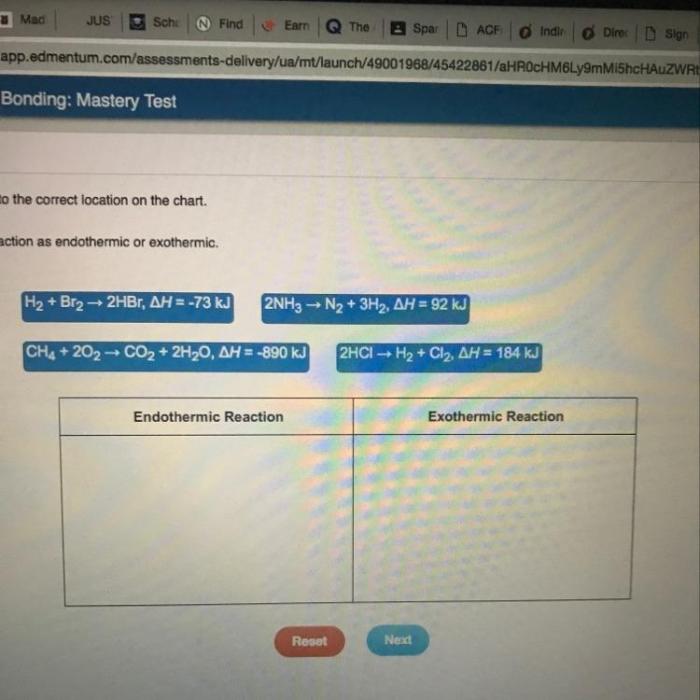
Classify each reaction as endothermic or exothermic: this fundamental concept in chemistry plays a pivotal role in understanding the energy dynamics of chemical reactions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of endothermic and exothermic reactions, providing a thorough exploration of their characteristics, examples, and applications.
By defining endothermic and exothermic reactions and highlighting their key differences, this guide lays the groundwork for a deeper understanding of these essential chemical processes.
Enthalpy Change in Chemical Reactions: Classify Each Reaction As Endothermic Or Exothermic
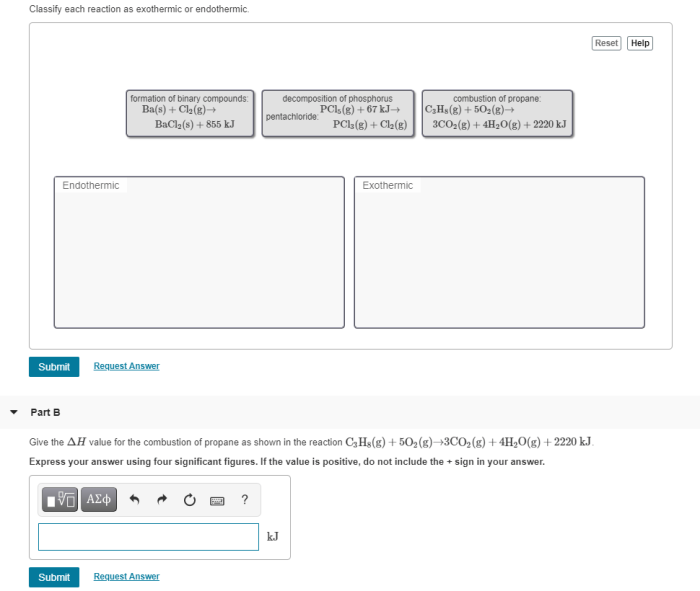
Chemical reactions involve changes in energy, which can be classified as endothermic or exothermic. These classifications depend on the heat flow between the system and its surroundings.
Endothermic reactions absorb heat from the surroundings, while exothermic reactions release heat into the surroundings.
Examples of Endothermic Reactions, Classify each reaction as endothermic or exothermic
- Melting of ice (H 2O(s) → H 2O(l)): ΔH = +6.01 kJ/mol
- Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water (NH 4Cl(s) → NH 4Cl(aq)): ΔH = +14.7 kJ/mol
- Photosynthesis (6CO 2+ 6H 2O + light → C 6H 12O 6+ 6O 2): ΔH = +2803 kJ/mol
Examples of Exothermic Reactions
- Combustion of methane (CH 4+ 2O 2→ CO 2+ 2H 2O): ΔH = -890 kJ/mol
- Neutralization of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid (NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H 2O): ΔH = -57.3 kJ/mol
- Respiration (C 6H 12O 6+ 6O 2→ 6CO 2+ 6H 2O): ΔH = -2803 kJ/mol
Factors Affecting the Enthalpy Change of a Reaction
- Type of reaction (e.g., combustion, neutralization)
- Reactant and product stoichiometry
- Physical state of reactants and products
- Temperature and pressure
- Presence of a catalyst
Applications of Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
- Endothermic reactions: Refrigeration, air conditioning, cooling packs
- Exothermic reactions: Combustion engines, fireworks, heat packs
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions?
Endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings, resulting in an increase in temperature. In contrast, exothermic reactions release energy into their surroundings, leading to a decrease in temperature.
How can I identify whether a reaction is endothermic or exothermic?
The enthalpy change (ΔH) of a reaction indicates whether it is endothermic or exothermic. A positive ΔH value indicates an endothermic reaction, while a negative ΔH value indicates an exothermic reaction.
What are some examples of endothermic reactions?
Melting of ice, dissolving of ammonium chloride in water, and photosynthesis are examples of endothermic reactions.
What are some examples of exothermic reactions?
Combustion of fuels, neutralization of acids and bases, and cellular respiration are examples of exothermic reactions.