Poverty cycle diagram ib economics – The poverty cycle diagram in economics serves as a powerful tool to understand the complex interplay of factors that perpetuate poverty. This article delves into the components, contributing factors, and consequences of the poverty cycle, while also exploring strategies to break free from its grip.
1. Definition of Poverty Cycle Diagram: Poverty Cycle Diagram Ib Economics
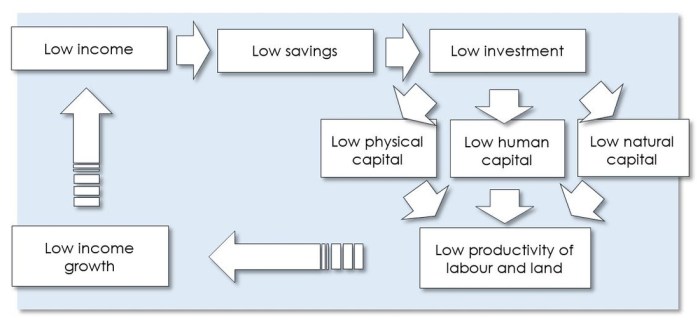
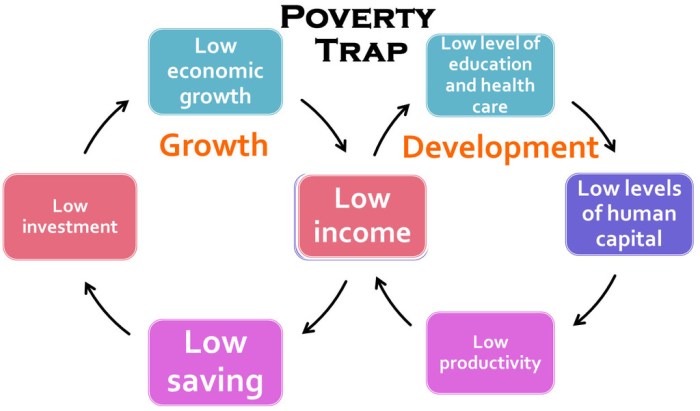
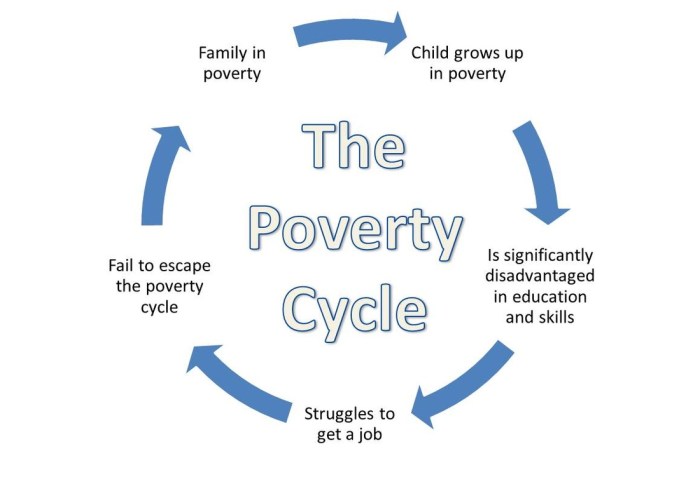
A poverty cycle diagram is a visual representation of the interconnected factors that contribute to and perpetuate poverty. It illustrates the complex interplay of economic, social, and environmental factors that trap individuals and communities in a cycle of deprivation.
2. Components of Poverty Cycle Diagram
Key components typically included in a poverty cycle diagram include:
- Low income and lack of economic opportunities
- Limited access to education and healthcare
- Poor housing and sanitation
- Social exclusion and discrimination
- Environmental degradation
3. Factors Contributing to Poverty Cycle, Poverty cycle diagram ib economics
Factors that contribute to the perpetuation of the poverty cycle include:
- Lack of access to quality education and skills training
- Discrimination and prejudice based on race, gender, or other characteristics
- Economic inequality and lack of social mobility
- Environmental degradation and climate change
4. Consequences of Poverty Cycle
The poverty cycle has severe consequences for individuals and society, including:
- Increased risk of disease, malnutrition, and premature death
- Lower educational attainment and reduced economic productivity
- Social instability and increased crime rates
Questions and Answers
What is the poverty cycle diagram?
The poverty cycle diagram is a visual representation of the interconnected factors that contribute to and perpetuate poverty.
What are the key components of the poverty cycle diagram?
The key components typically include lack of education, unemployment, low income, poor health, and inadequate housing.
How can education help break the poverty cycle?
Education provides individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to secure better-paying jobs, improve their economic opportunities, and break free from the cycle of poverty.