Quiz 3 the great depression – Quiz 3: The Great Depression transports us back to a tumultuous era in American history, a time of widespread economic hardship and profound societal change. This comprehensive quiz delves into the intricate web of causes, consequences, and cultural reverberations of the Great Depression, shedding light on its enduring legacy.
Unraveling the complexities of this defining period, we will explore the historical context that sowed the seeds of the economic crisis, dissect the major causes and consequences that shook the nation, and examine the government’s response in an attempt to mitigate the devastation.
Moreover, we will delve into the cultural impact of the Great Depression, tracing its influence on art, literature, and music, and uncovering the lasting cultural legacy it left behind.
Historical Context
The Great Depression, a global economic crisis that began in the United States in the 1930s, was the result of a complex interplay of economic and social factors.
The decade leading up to the Depression was marked by rapid economic growth and speculation, particularly in the stock market. However, this growth was built on shaky foundations, including unsustainable levels of consumer debt and overproduction in key industries.
Triggering Events
The stock market crash of 1929, often referred to as Black Tuesday, is widely seen as the trigger for the Great Depression. The crash wiped out billions of dollars in wealth and caused a loss of confidence in the financial system.
Other factors that contributed to the crisis include the Federal Reserve’s tight monetary policy, which raised interest rates and made it more difficult for businesses to borrow money; the Smoot-Hawley Tariff, which raised tariffs on imported goods and led to a decline in international trade; and the collapse of the banking system, which left many people unable to access their savings.
Impact on Society
The Great Depression had a devastating impact on all sectors of society. Unemployment soared, reaching 25% at its peak, and millions of people lost their homes and savings.
The crisis also led to a decline in economic activity, as businesses closed and investment dried up. This had a ripple effect on other industries, such as agriculture and manufacturing.
The Great Depression also had a significant social impact. It led to increased poverty, homelessness, and crime. It also eroded public trust in the government and the financial system.
Causes and Consequences: Quiz 3 The Great Depression

The Great Depression, a decade-long economic crisis, emerged from a complex interplay of domestic and international factors. Its consequences left an enduring impact on the American economy and society.
Causes
Domestically, the 1920s witnessed a period of rapid economic expansion, fueled by consumer spending and speculation in the stock market. However, this unsustainable growth led to an overproduction of goods and a collapse in demand.
The third quiz on the Great Depression is coming up soon, and I’m feeling a bit nervous. I’ve been studying hard, but I could use some extra help. I’m thinking about checking out the Kaplan Advanced Math CC A course.
It’s supposed to be really good, and I’m hoping it will give me the edge I need to ace this quiz. I’m determined to do well on this quiz and show my professor what I’m made of.
- Overproduction:Industries produced more goods than consumers could buy, leading to a glut in the market.
- Stock Market Crash:In October 1929, the stock market crashed, wiping out billions of dollars in wealth and eroding public confidence.
- Banking Crisis:The failure of banks due to bad loans and a lack of regulation led to a loss of trust in the financial system.
Consequences
The Great Depression had devastating consequences for the United States:
- Unemployment:Joblessness skyrocketed, reaching nearly 25% at its peak in 1933.
- Poverty:The loss of income plunged millions into poverty, leading to widespread homelessness and hunger.
- Social Unrest:Economic hardship fueled social unrest, including protests, strikes, and a rise in crime.
Long-Term Effects, Quiz 3 the great depression
The Great Depression had a profound impact on the American economy and society:
- Economic Reforms:The crisis led to the implementation of New Deal policies aimed at regulating the economy and providing social welfare.
- Social Changes:The Depression challenged the traditional values of individualism and self-reliance, fostering a greater sense of collective responsibility.
- Political Legacy:The Depression contributed to the rise of President Franklin D. Roosevelt and the Democratic Party, shaping American politics for decades.
Government Response
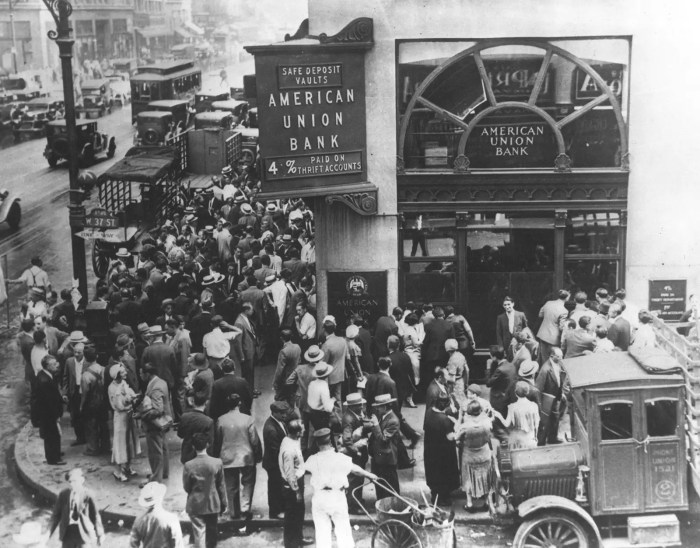

The Great Depression triggered a profound government response, with the implementation of various policies and programs aimed at mitigating its devastating effects.
The New Deal
The New Deal, a series of economic and social reforms introduced by President Franklin D. Roosevelt, played a pivotal role in shaping the American economy and society. The New Deal’s primary objectives were to provide relief to the unemployed, stimulate economic recovery, and reform the financial system.
- Relief Programs:The New Deal established a comprehensive system of relief programs, including the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), which provided employment to young men in conservation projects, and the Works Progress Administration (WPA), which created jobs in infrastructure and public works projects.
- Stimulus Measures:The New Deal included a range of stimulus measures, such as the Public Works Administration (PWA), which invested in large-scale infrastructure projects, and the Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA), which aimed to raise agricultural prices by reducing production.
- Financial Reforms:The New Deal introduced significant financial reforms, including the creation of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) to protect bank deposits, and the Glass-Steagall Act to separate commercial and investment banking.
Effectiveness of Government Policies
The effectiveness of government policies in addressing the Great Depression remains a subject of debate. While some policies, such as the CCC and WPA, provided immediate relief to the unemployed, their long-term impact on economic recovery is less clear.
Critics argue that the New Deal’s focus on deficit spending and government intervention contributed to the slow pace of recovery. However, supporters contend that the New Deal prevented a deeper and more prolonged economic downturn and laid the foundation for future economic growth.
Cultural Impact
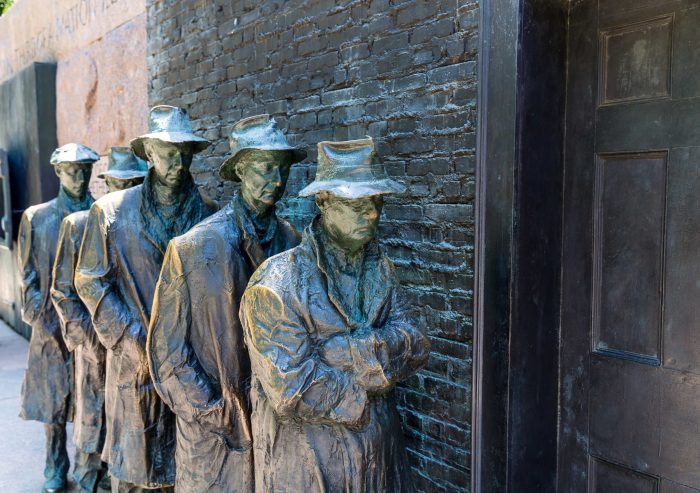

The Great Depression left an indelible mark on American culture, shaping its art, literature, and music. The economic crisis and social upheaval of the era gave rise to powerful artistic expressions that reflected the struggles, hopes, and fears of the American people.
Art
During the Depression, artists turned to realism and social commentary to depict the harsh realities of life. Paintings like Grant Wood’s “American Gothic” (1930) captured the somber mood of rural America, while Dorothea Lange’s photographs, such as “Migrant Mother” (1936), exposed the plight of the poor and dispossessed.
Literature
The Great Depression inspired a wave of literary works that explored themes of poverty, social injustice, and the search for meaning. John Steinbeck’s novel “The Grapes of Wrath” (1939) chronicled the struggles of migrant farm workers, while F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby” (1925) portrayed the decadence and disillusionment of the Jazz Age.
Music
The Great Depression also influenced American music. Jazz, with its improvisational and experimental nature, provided a soundtrack for the era’s uncertainty and anxiety. Blues music, rooted in the experiences of African Americans, expressed the pain and resilience of a marginalized community.
Folk songs, such as Woody Guthrie’s “This Land Is Your Land,” became anthems of protest and hope.
Legacy
The cultural legacy of the Great Depression continues to shape American society. The art, literature, and music of the era remain powerful reminders of the human spirit’s ability to endure adversity and strive for a better future.
Questions and Answers
What were the primary causes of the Great Depression?
The Great Depression was sparked by a complex interplay of domestic and international factors, including the collapse of the stock market, excessive speculation, weak banking regulations, and global economic imbalances.
How did the Great Depression impact American society?
The Great Depression led to widespread unemployment, poverty, and social unrest. It shattered the dreams of millions of Americans and left an enduring scar on the nation’s psyche.
What role did the government play in addressing the Great Depression?
The government implemented a series of policies and programs under the New Deal, including job creation initiatives, financial reforms, and social welfare programs, to combat the effects of the Great Depression.
How did the Great Depression influence American culture?
The Great Depression profoundly impacted American culture, inspiring works of art, literature, and music that reflected the experiences and emotions of the time. It left a lasting legacy in the nation’s artistic and cultural landscape.
